Interfacing a TFT_320QVT LCD/Touchscreen/SD to a Teensy 3.0

You can write a book review and share your experiences. Other readers will always be interested in your opinion of the books you've read. Whether you've loved the book or not, if you give your honest and detailed thoughts then people will find new books that are right for them. ImageConverter Plus is a easy to use professional image conversion tool. It supports a large number of file formats. Not only does it convert images to different file formats it does have image editing options also. The most common ones being resize, rotate, crop, color effect, gamma, watermark etc. ImageConverter Plus in a netshell.
I’m working on a project which needs a touchscreen LCD. After searching eBay for a while, I noticed that many vendors were selling basically the same 3.2″ 320×240 TFT with resistive touchscreen and SD card reader. Though there were slight variations in the silkscreens, they all had the same model number – TFT_320QVT. I bought mine from digitalzone88 for $12.29. The board uses a SSD1289 LCD driver IC, and runs on 3.3V. The 3.3V voltage is incompatible with the typical Arduino, which runs at 5V (some vendors have created shields to interface it to an Arduino Mega). However, I purchased the TFT_320QVT with the intention of interfacing it to a Teensy 3.0, which runs at 3.3V. I noticed that there were not enough through-hole I/O pins on Teensy 3.0 to simultaneously interface to the LCD, touchscreen, and SD card. This necessitated the usage of the Teensy 3.0’s additional I/O pins, accessible only via solder pads on its underside: To facilitate access to the 14 solder pads, I attached some header pins to piece of stripboard, and soldered 40AWG wire-wrap wire to between the pads and headers: The Teensy 3.0 runs on PJRC’s specially modified version of Arduino – Teensyduino. The task was to find compatible Arduino libraries. First order of business was the LCD. I searched the web, and found that dawnmist had spent a considerable effort in modifying Henning Karlson’s UTFT to work with the Teensy 3.0. Unbeknownst to me at the time, dawnmist’s modified UTFT is actually bundled with Teensyduino!
Next, was to get the touch screen working. It turns out that the current version of Henning Karlson’s UTouch is compatible with the Teensy 3.0.
For the SD slot, I tried the version of the Arduino SD library that’s bundled with Teensyduino. Unfortunately, though the SD library works with the TFT_320QVT’s SD reader, it stops working if you instantiate a UTFT object in the sketch. I tried sdfatlib, and found that not only does it work w/ the Teensy 3.0, but it coexists fine with UTFT. The only catch I found is that it works only with SPI_HALF_SPEED. When I set it to SPI_FULL_SPEED, it stops working.
Here is the Teensy 3.0 running UTFT‘s demo sketch on the TFT_320QVT:
Below is the step-by-step procedure to getting the TFT_320QVT up and running with Teensy 3.0:
Step 1: Install the libraries
1. UTFT: Run the Teensyduino installer, and when the Libraries to Install dialog is displayed, check the box next to UTFT in the Choose Additional Libraries to Install combobox. (Note: Henning Karlson’s latest UTFT also works with Teensy 3.0, but my discussion below will show how to interface to the UTFT that’s bundled with Teensyduino 1.18).
2. UTouch: Download UTouch.rar. Use WinRar or 7-zip to extract the enclosed UTouch folder. From the Arduino IDE pull-down menu, use Sketch->Import Library->Add Library… to install the extracted UTouch folder. Alternatively, you can just copy Utouch/ to your arduinosketchbook/libraries directory.
3. sdfatlib: Download the latest version of sdfatlib. From the Arduino IDE pull-down menu, use Sketch->Import Library->Add Library… to install the downloaded sdfatlibyyyymmdd.zip file. You can alternatively just extract the SdFat/ folder into your arduinosketchbook/libraries directory.
Step 2: Wire it up
1. LCD: dawnmist‘s modified UTFT library that’s bundled with Teensyduino has a configuration file: arduinofolderlibrariesUTFThardwarearmHW_Teensy3.h. Inside HW_Teensy3.h, there are 3 options for the LCD pin assignments: USE_B_D_PORTS, USE_C_D_PORTS, and USE_USER_PORTS. By default, the file has
#define PORTS USE_B_D_PORTS
enabled. USE_B_D_PORTS gives the best performance when your sketch needs to use SPI (which is needed for the SD card slot). USE_C_D_PORTS gives the fastest performance, but is incompatible with SPI. USE_USER_PORTS allows you to configure arbitrary pins (by changing the DB_0-DB_16 #defines), but results in the slowest performance. I elected to use the default USE_B_D_PORTS setting.
2. SD card reader: The SD card reader works via SPI, so it needs to use SD_DIN->DIN (MOSI – 11), SD_DO->DOUT (MISO – 12), SD_CLK->SCK (13), and one of the chip select pins, CS0-CS4 (10,9,20,21, or 15). I chose to use SD_CS->CS4 (15).
3. Touchscreen: The touchscreen uses 5 pins, T_DIN/T_DO,T_CS/T_CLK/T_IRQ, which can be assigned to any arbitrary free GPIO pins.
Below is a chart of my pin assignments:
Teensy_pin = TFT_320QVT_pin
0 = LCD_DB4
1 = LCD_DB5
2 = LCD_DB8
3 = LCD_LED_A (backlight)
5 = LCD_DB15
6 = LCD_DB12
7 = LCD_DB10
8 = LCD_DB11
9 = LCD_REST (RESET)
11 = SD_DIN (MOSI)
12 = SD_DO (MISO)
13 = SD_CLK (SCK)
14 = LCD_DB9
15 = SD_CS
16 = LCD_DB0
17 = LCD_DB1
18 = LCD_DB3
19 = LCD_DB2
20 = LCD_DB13
21 = LCD_DB14
22 = LCD_WR
23 = LCD_RS
24 = T_CLK
25 = LCD_DB7
26 = T_CS
27 = T_DIN
28 = T_DO
29 = T_IRQ
32 = LCD_DB6
LCD_RD needs to be pulled up to 3.3v
I have created a sketch, UTFT_UTouch_SdFat_teensy3, that simultaneously demonstrates the LCD, touchscreen, and SD card by modifying the UTouch demo sketch. Below are the lines which are critical to configuring it to work with the above pin connections:
The file displays a bitmap, ade.raw, as the background. Before running the sketch, copy ade.raw to a FAT-formatted SD card, and insert it into the TFT_320QVT’s SD card slot.
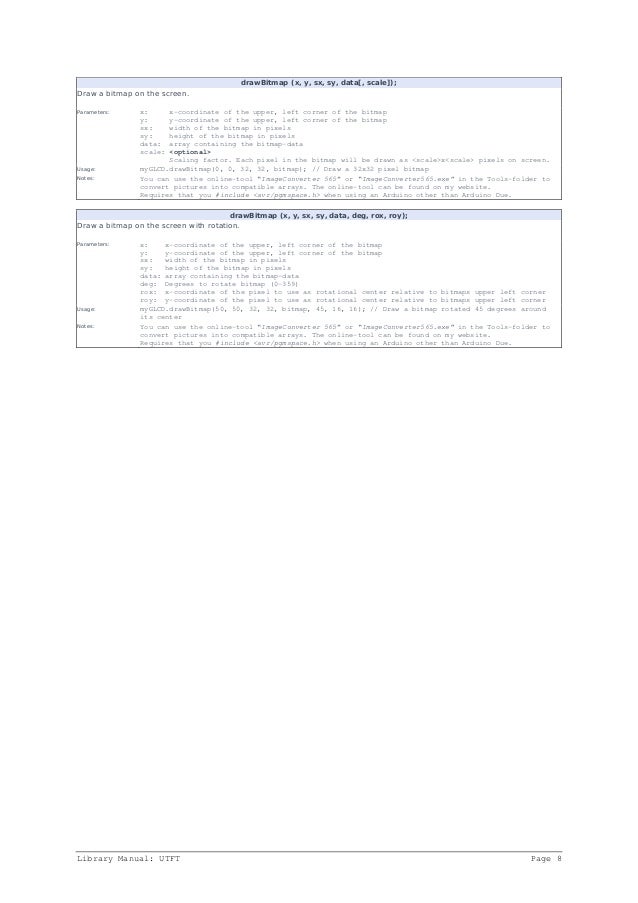
You can also substitute your own bitmap file. To create a .raw file, first create a 240×320 pixel jpg, png, or GIF file. Run it through either imageconverter565.exe (bundled with UTFT) or the online ImageConverter 565 make sure to select Convert to .raw file and Target Platform Arduino (AVR).
Here’s what UTFT_UTouch_SdFat_teensy3 looks like when it’s running:
Many thanks to dawnmist, and the others who figured out how to get UTFT working with the Teensy 3.0.

Downloads:
UTFT_UTouch_SdFat_teensy3
UTFT_demo_tft_320qvt_teensy3
Links:
I obtained much of the information I needed from these pages:
dawnmist – screen working … finally
Teensy 3.0 – driving an SSD1289 with utft
This program will convert a 24-bit bmp (the most common variant) and convert it to a 16-bit bitmap.
1. Choose the 24-bit bmp you wish to convert
2. Choose the destination directory and convert.
3. Put the bmp on an SD-card and use DmTftLibrary to display the images on your display.
Here is a download link for the .msi: DisplayModule's Image Converter (.msi file zip DisplayModule's Image converter 1.0, smaller download size)
Image Converter 565 online, free
There are 2 reasons for converting your images to 16-bit bmp with flipped row order:- 1. Size.
The image is only 2/3 of the original size and because most embedded displays/drivers uses 16-bit color, the picture quality will be the same.
- 2. Speed.
Most embedded TFT uses the 16-bit 565 format and support the top-bottom write order.
a, The MCU does not need to convert the 24-bit to 16-bit 565, this is already done.
b, If the source format is already in correct order, a faster algorithm for reading the data can be used.
c, There is less data to read (because the image is only 2/3 of an original size)
Compared to raw picture data there are several advantages:
Image Converter 565 Online Youtube Downloader
a, It has meta data about the format, size, how it is stored etc. With raw data, the program must already know this.
b, It is a standard so it can be viewed directly in most viewer (although not all viewer )
c, Can create and edit the images in advanced photo editing programs like photoshop.
Source file:
Have to be a 24-bit bitmap with row order bottom-top. This is by far the most common format.
Destination file:
A file with the same image information will be created:
- It will use bitmap HEADERINFOV 3
- It will be 16-bit 565 format
- It will have reversed row order (top-bottom)
This file can be read by many programs, but not many programs can create this file. Photoshop is one of the programs which can create it.
Program options:
- Convert to C-source code, will take the 24-bit bitmap and create an array C-source file. No modifications will be done
- Convert to C-source code (16-bit 565 top-bottom bitmap), will convert the image to 16-bit and then store it as a C-source file.
- Arduino C-source hack, will replace some 0xFF with 0xFE so that the C-source can be downloaded to the Arduino Flash. Otherwise this might get a download error (because the AVRDude settings Arduino is using)
3.4 inch 800*800 round SFT (Super-Fine TFT) touch display for vehicle or special occasion .

Jpeg File Converter Free
0.95 96*64 16 bit Color OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) display
24 Bit Bmp Converter
7.5 Inch 640*384 E-Ink